Timers - Introduction
Resources: none
Goal
To understand the general operation of timers/counters.
Timers/counter
Generally speaking, timers are binary counters that count up/down in single steps to a top value and will start over again. This principle is depicted in the following block diagram.
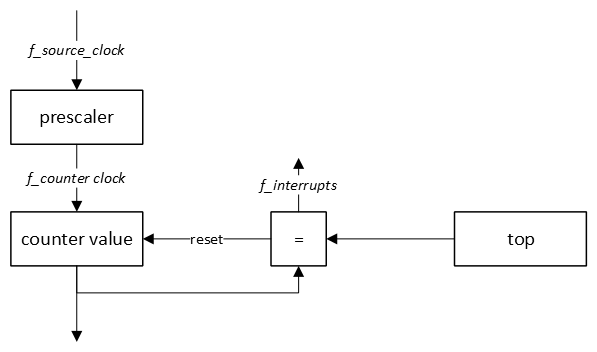
The frequency at which interrupts are generated (f_interrupts) is equal to:
f_interrupts = f_source_clock / prescaler / (top + 1)
Or rewritten to the time between two interrupts (T_interrupts):
T_interrupts = T_source_clock * prescaler * (top + 1)
The number of pulses counted by most timers is equal to (top + 1), because the timer starts counting from 0. This, however, is implementation dependent.
For a timer that counts up, the following general timing diagram is applicable.
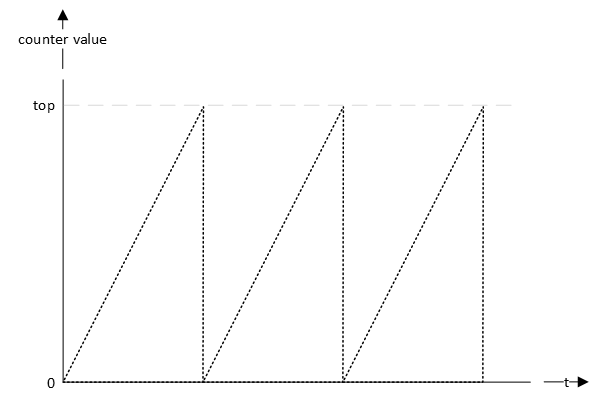
Although this simplified basic representation is applicable for all timers, implementations of timer modules range from very basic to very complex. Timers can be used to capture and/or generate a variety of signals, such as square waves, PWM signals, pulse counting, etc.